Why is it Important to Monitor Blood Pressure after a Stroke?
It is important to monitor blood pressure after a stroke because high blood pressure is a major risk factor for stroke and can also lead to recurrent stroke if not properly managed. In addition, blood pressure that is too low can also cause problems, such as dizziness and fainting, which can increase the risk of falls and further injury. Therefore, it is important to maintain blood pressure within a healthy range to reduce the risk of stroke and other complications.
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the measurement of pressure the blood puts on the walls of the vessels as the blood moves around the body. When the heart pumps blood with each heartbeat, the blood is pushed through large blood vessels of the circulatory system, which provides blood and oxygen to organs and tissues throughout the body. [1]
One of the risk factors for having a stroke is hypertension. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is when the force of blood flowing through your blood vessels is too high. Nearly 50% of American adults have high blood pressure, and many don’t even know they have it. [2]
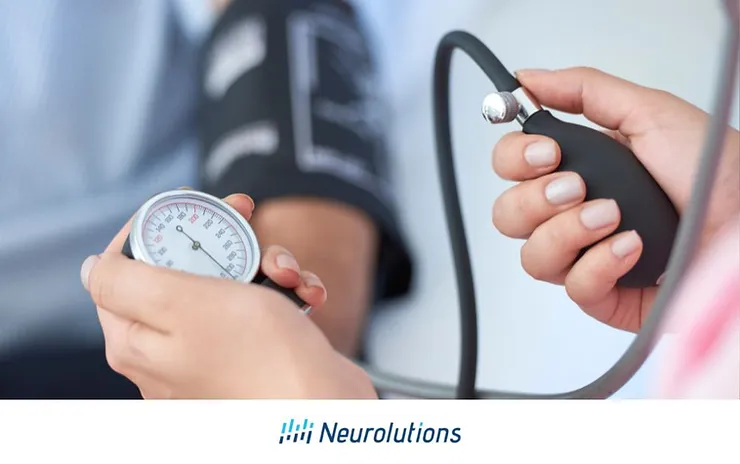
The best way to understand if you have blood pressure is to have your blood pressure checked. When you visit your health care professionals routinely, you will always have your blood pressure checked. After having a stroke, or any change to your blood pressure medications, it’s best to be active with blood pressure monitoring at home.
Monitoring Blood Pressure – The Science Behind the Measurement
It’s important to understand the blood pressure monitoring basics. When you have your blood pressure taken, you will notice readings are all given with two numbers. The first number is the “top number” followed by the second number is the “bottom number”
Blood pressure measurement always includes these two numbers. The top number, or “systolic blood pressure” is the measurement of force when the heart is pushing and pumping the oxygen-rich blood into the blood vessels. The bottom number, or “diastolic blood pressure” is the measurement of pressure on the walls of the blood vessels when the heart muscle relaxes, and is not pumping blood.
Home blood pressure monitors are a great way to monitor your blood pressure at home. To use a home blood pressure monitor it is important to measure your blood pressure three different times a day (morning, mid-day, and evening) every day. After each reading, record your results on a blood pressure log. We have included a printable blood pressure log that you can download here.
For at-home blood pressure monitor accuracy, it is important when taking your blood pressure to:
- Don’t smoke, drink caffeinated beverages, or exercise within 30 minutes before measuring your blood pressure. [3]
- Empty your bladder and rest quietly for 5 minutes before taking your blood pressure measurement. [3]
- Sit correctly with your back straight, with both feet flat on the floor. Do not cross your legs. Your arm you use to take your blood pressure should be supported on a flat surface (like a table) with your upper arm at heart level. [3]
- Do not take your blood pressure over clothes. [3] Ensure your blood pressure cuff is just above the bend of your elbow.
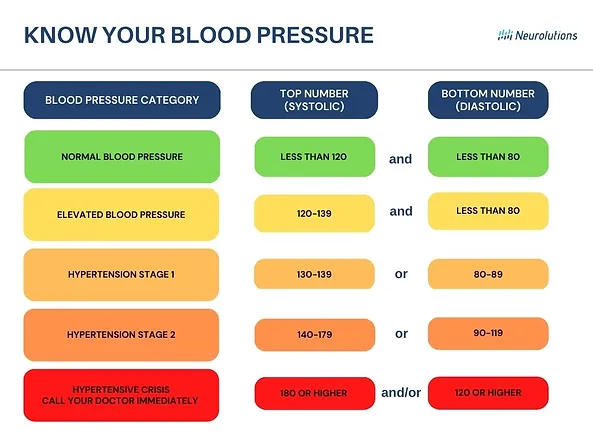
What is Normal Blood Pressure?
Normal Blood Pressure is considered LESS THAN 120 (top number) and LESS than 80 (bottom number).
Elevated (not high blood pressure) is considered 120-129 (top number) and LESS than 80.
What is High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure is when either the top number is 130 or higher or if the bottom number is 80 or higher. The difference here is that if either the top number or the bottom number is high, it is considered high blood pressure.
There are different stages of high blood pressure.
Stage 1 – Top Number is 130-139 or Bottom Number is 80-89
Stage 2 – Top Number is 140 -179 or Bottom Number is 90-119
Stage 3 – Crisis. Consult your doctor immediately. The top number is higher than 180 and/or the Bottom Number is higher than 120.
What is Low Blood Pressure
There is a consistent daily number of your blood pressure that is considered too low if you are not experiencing any of the below symptoms. Low Blood pressure is when the top number is 90 or less with a bottom number 60 or less. Here are the symptoms of low blood pressure:[4]
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Fainting
- Dehydration and unusual thirst
- Lack of concentration
- Blurred vision
- Cold, clammy, pale skin
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Fatigue
- Depression
Sometimes low blood pressure can be caused by certain medications in combination with other medications, alcohol, and over-the-counter medications. If you are experiencing any low blood pressure with any of the above symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
How to Manage Your Blood Pressure
Always monitor your blood pressure daily while using the blood pressure chart. If your doctor has prescribed blood pressure medication, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions.
Exercise to Manage Blood Pressure
Exercising is a great way to maintain a healthy weight and lower your blood pressure. It is recommended to exercise for at least 90-150 minutes per week of aerobic exercise and resistance strength exercises approximately every other day. [5]
Diet to Manage Blood Pressure
Eating healthy is a lifestyle change that will help your blood pressure and many other health risk factors. Eating lots of fresh fruit, vegetables, and foods that are low in saturated fats is recommended.
Most importantly, reducing your daily intake of sodium is good for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Try to stay under 1,500mg of sodium per day. Instead of seasoning your food with salt, using alternative spices that do not contain sodium is recommended. [5]
Limiting alcohol intake is also important. Drink no more than 1 alcoholic beverage per day if you are a woman. For men, drink no more than 1-2 drinks per day. [5]
Supplements to Manage Blood Pressure
There are many supplements that may or may not help lower blood pressure. This does not mean that these supplements are safe. You should always talk to your healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your routine. As serious side effects or interactions with your medications can occur.
What Factors Affect Your Blood Pressure?
Managing your risk factors for high blood pressure is very important. Here are the top risk factors that may increase your blood pressure and cause hypertension: [6]
- Diabetes
- Unhealthy diet
- Lack of physical activity and/or exercise
- Obesity
- Alcohol use
- Tobacco use
- Family history of hypertension
References:
[1] InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. What is blood pressure and how is it measured? 2010 Jun 24 [Updated 2019 May 23]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279251/
[2] https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/the-facts-about-high-blood-pressure
[6] https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/risk_factors.htm